Detailed Explanation and Classification of the Lower Yard in the Mining Area - Black King Kong Broadcast
Preface
In the complex system of mining operations, the lower section of the mining area plays a crucial and irreplaceable role. It acts as a key hub in the mining process, connecting the upper section of the mining area with the stage transportation roadway, responsible for the transfer of coal, gangue, and materials. It is also a key location for personnel movement and vehicle scheduling, serving as the core link for mining and auxiliary transportation. Rational design of the lower section of the mining area is of great significance in improving the efficiency, safety, and economy of mining operations, directly affecting the stable operation and profitability of the entire mining production system. Therefore, in-depth exploration of the concept and classification of the lower section of the mining area is an important prerequisite for mining engineers to master advanced mining technologies and optimize mining processes.
Concept of the Lower Section of the Mining Area
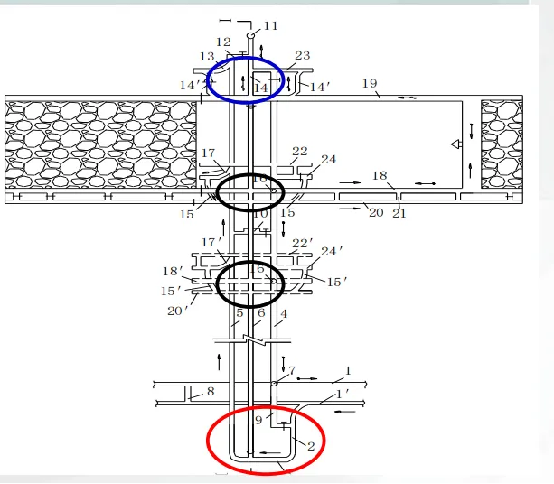
(Image from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
(1) Definition Explanation
The lower section of the mining area is a collective term for a group of roadways and chambers connecting the upper section of the mining area and the stage transportation roadway. It is a key component of the mining production system. From the perspective of the entire mining operation process, the upper section of the mining area is responsible for lifting and transporting the coal and gangue mined from the mining area, while the stage transportation roadway is responsible for transporting these materials to the bottom roadway or other processing locations. The lower section of the mining area acts as a bridge between the two, effectively connecting the internal transportation system of the mining area with the main transportation system of the entire mine, ensuring the continuity of mining production. Taking the common underground coal mining as an example, after the coal is mined from the coal face, it is transported to the upper section of the mining area via scraper conveyors, belt conveyors, etc., and then transferred to the stage transportation roadway via the lower section of the mining area, and finally transported to the surface. If the entire mining system is compared to the human body, then the lower section of the mining area is like the human joints, an important hub for the coordinated operation of various parts.
(2) Constituent Elements
The lower section of the mining area includes various roadways and chambers, which cooperate with each other to achieve the functions of the yard. The dump track is an inclined roadway connecting the upper section of the mining area and the storage track. Its function is to allow mine cars to smoothly transition between lines at different heights, achieving vehicle turning and lifting and lowering. The storage track is a line used for parking mine cars, divided into empty car storage tracks and loaded car storage tracks. According to the production capacity and transportation needs of the mining area, the storage track needs to have a certain length to ensure that a sufficient number of mine cars can be parked to meet the transportation turnover. The connecting roadway is used to connect roadways and chambers with different functions, forming a complete transportation network to ensure smooth ventilation, pedestrian traffic, and transportation.
Various chambers also play an indispensable role in the lower section of the mining area. The coal bin is used to store coal, buffering the imbalance between mining area production and transportation, and ensuring the stability of transportation; the winch room houses the hoisting winch, providing power for the lifting and lowering of mine cars; the substation is responsible for providing power to the yard and equipment in the mining area, ensuring the normal operation of the equipment. These roadways and chambers are interconnected: the dump track introduces mine cars from the upper section of the mining area into the storage track, the connecting roadway connects the storage track with various chambers, the coal bin stores coal, which is then loaded onto the storage track through related equipment, the winch room controls the transportation of mine cars, and the substation provides energy support, together forming the complex and orderly system of the lower section of the mining area.
Classification of the Lower Section of the Mining Area
The classification methods for the lower section of the mining area are diverse; different types can be divided according to different standards. Common classification criteria include transportation methods and the location of material yards. These classification methods do not exist in isolation but are interrelated, together forming a rich classification system for the lower section of the mining area to adapt to the complex and changing needs of mining production. Different types of lower sections of mining areas have different functions, applicable scenarios, and design points. This requires mining engineers to consider and select the most suitable yard type based on specific geological conditions, production scale, and technical requirements to ensure the efficient and stable operation of the mining area transportation system.
(1) Classification Based on Transportation Methods
1. Belt Conveyor Coal Transportation
• Coal Bin Bottom Transfer In this method, coal is transported from the upper section of the mining area to the coal bin for storage via a belt conveyor. When it needs to be transferred, the coal is released from the bottom of the coal bin, and a feeder, etc., loads the coal onto another belt conveyor, which is then transported to the stage transportation roadway. This method is suitable for situations where the mining area has a large production capacity and has certain requirements for coal storage. Its advantage is that it can buffer the imbalance between mining area production and transportation. When the mining area produces more coal, the coal bin can temporarily store the coal to avoid congestion of transportation equipment; when the transportation capacity of the transportation roadway is limited, the coal bin can also play a regulating role. However, it also has limitations, such as the high construction and maintenance costs of the coal bin, and the possibility of equipment failure during transfer, affecting the continuity of transportation.
• Direct Connection Direct connection refers to the direct connection of the belt conveyor in the upper section of the mining area with the belt conveyor in the stage transportation roadway. Coal is directly transferred from the belt conveyor in the upper section of the mining area to the belt conveyor in the stage transportation roadway without going through the coal bin storage stage. This method is suitable for situations where the production capacity of the mining area is relatively stable, the distance between the mining area and the transportation roadway is relatively short, and the terrain conditions are relatively simple. Its advantages are fewer transportation links, continuous coal transportation, high efficiency, and relatively low equipment investment and operating costs. However, its limitations lie in the high requirements for the stability of the transportation system; once a section of the belt conveyor fails, the entire transportation system will be interrupted; and due to the lack of coal bin buffering, the production capacity of the mining area and the transportation capacity of the transportation roadway need to be highly matched, otherwise, transportation problems may easily occur.
2. Mine Car Coal Transportation
• Roadway Loading Type Main roadway loading-type lower yard in the mining area: Coal is loaded from the lower outlet of the mining area coal bin onto mine cars, and the mine cars are directly loaded in the main roadway. In terms of line layout, there are special loading lines in the main roadway, generally including empty car storage lines, loaded car storage lines, and loading points. Common shunting methods include electric locomotive shunting, pusher shunting, dispatching winch shunting, and automatic rolling shunting. The advantages of this type are simple layout, small engineering volume, and relatively low investment; the disadvantages are that the main roadway transportation and mining area loading interfere with each other to a greater extent. When main roadway transportation is busy, it may affect the loading efficiency of the mining area, and the throughput capacity of the main roadway is required to be high. It is suitable for mines with smaller mining area production capacity and less busy main roadway transportation.
• Stone gate loading type Stone gate loading type: The characteristic of the stone gate loading type is that the loading point is set in the stone gate perpendicular to the main roadway. In terms of line layout, there are corresponding storage lines and loading equipment in the stone gate. After the coal from the mining area coal bin is loaded into the mine cars, it is transported to the stone gate loading point by rail. Shunting is relatively flexible, and appropriate shunting methods can be selected according to the actual situation. The advantages are that the main roadway transportation and mining area loading are relatively independent and interfere with each other less, which can improve the loading efficiency and the throughput capacity of the main roadway; the disadvantages are that the excavation workload of the stone gate is large and the cost is high. It is suitable for mines with large mining area production capacity, busy main roadway transportation, and conditions for excavating stone gates.
• Detour loading type Detour loading type: The detour loading type refers to setting a detour on one side of the main roadway to carry out loading operations. The line layout is relatively complex, including the connecting lines from the uphill track to the detour, the storage lines and loading lines in the detour, etc. The shunting process needs to be realized through reasonable line design and scheduling. The advantages are that it does not affect the normal transportation of the main roadway, the loading operation is relatively independent, and the transportation efficiency can be improved; the disadvantages are that the excavation and maintenance workload of the detour is large, the investment cost is high, and the line layout is complex, and the shunting difficulty is large. It is suitable for mines with large mining area production capacity, high requirements for the throughput capacity of main roadway transportation, and sufficient space to arrange detours.
(II) Other classification dimensions
According to the different locations of the material yard, the lower yard in the mining area can be divided into top detour and bottom detour. Top detour refers to the material yard set in the detour on the top of the main roadway. This method is suitable for situations where the top surrounding rock conditions are good and it is easy to excavate and maintain the detour. Its advantages are that it can utilize the relatively stable rock layer on the top, reduce the cost of roadway support, and the connection with the main roadway is relatively convenient; the disadvantage is that if the top is not managed well, safety hazards such as top collapse may occur. Bottom detour is when the material yard is set in the detour on the bottom of the main roadway. It is used when the bottom rock layer is stable and it is more reasonable to transport materials from the bottom detour. Its advantage is that it can avoid complex geological conditions on the top and reduce the impact of top accidents on material transportation; the disadvantage is that the excavation difficulty of the bottom detour may be greater, and the arrangement of auxiliary facilities such as drainage is relatively complex.
Application cases of different types of lower yards in mining areas
(I) Case selection
In order to gain a deeper understanding of the actual application effects of different types of lower yards in mining areas, we selected three representative mine cases, each corresponding to a type of lower yard in the mining area. A Coal mine adopts the main roadway loading type lower yard in the mining area. The mine is located in North China, the coal seam is stably deposited, the dip angle is small, the mining area production capacity is relatively small, and the main roadway transportation is not busy. B Coal mine adopts the stone gate loading type lower yard in the mining area. It is located in the southwest mountainous area, the geological conditions are relatively complex, the coal seam dip angle is large, the mining area production capacity is large, and the main roadway transportation is busy. C Coal mine adopts the detour loading type lower yard in the mining area. It is located in the northwest region, the minefield area is large, the mining area production capacity is large, the requirements for the throughput capacity of main roadway transportation are high, and there is sufficient space to arrange detours.
(II) Case analysis
A The main roadway loading type lower yard in the mining area of the coal mine has a relatively simple line layout, with loading points and storage lines directly set in the main roadway. In actual operation, the initial construction cost is low, the engineering volume is small, and it can be put into use quickly. However, with the gradual expansion of the mining scale, the interference problem between main roadway transportation and mining area loading has become increasingly prominent, especially during peak transportation periods, vehicle congestion in the main roadway leads to a decrease in the loading efficiency of the mining area, affecting the overall production progress of the mine. In addition, due to the frequent traffic of vehicles in the main roadway, safety hazards have also increased relatively.
B The stone gate loading type lower yard in the mining area of the coal mine is vertically arranged with the stone gate and the main roadway, and the loading point is set in the stone gate. This design effectively reduces the mutual interference between main roadway transportation and mining area loading, and improves the loading efficiency and the throughput capacity of the main roadway. In actual production, the mine's transportation system is relatively smooth, coal can be transported in time, and the high-yield and high-efficiency of the mine is ensured. However, the excavation workload of the stone gate is large, the initial investment cost is high, and the maintenance difficulty of the stone gate is relatively large, requiring a lot of manpower, material resources, and financial resources.
C The detour loading type lower yard in the mining area of the coal mine sets a detour on one side of the main roadway for loading operations. The biggest advantage of this design is that it does not affect the normal transportation of the main roadway, the loading operation is relatively independent, and the transportation efficiency is high. In actual operation, even if the main roadway transportation is busy, the mining area loading can proceed smoothly, greatly improving the overall production capacity of the mine. However, the excavation and maintenance workload of the detour is large, the investment cost is high, and the line layout is complex, and the requirements for scheduling and management are high. If the scheduling is not proper, problems such as vehicle congestion may occur.
Through the analysis of these three cases, it can be seen that different types of lower yards in mining areas have their own advantages and disadvantages in practical applications. The main roadway loading type is suitable for mines with small mining area production capacity and not busy main roadway transportation, but its limitations will gradually become apparent as the production scale expands; the stone gate loading type is suitable for mines with large mining area production capacity and busy main roadway transportation, and can effectively solve the transportation interference problem, but the cost is high; the detour loading type is suitable for mines with large mining area production capacity and high requirements for the throughput capacity of main roadway transportation, with high transportation efficiency, but high construction and management difficulty. In actual mining engineering, according to the specific conditions of the mine, geological conditions, production scale, transportation needs and other factors should be comprehensively considered to select the most suitable type of lower yard in the mining area to achieve safe and efficient production of the mine.
Summary
The lower roadway of the mining area serves as a crucial connecting hub between the uphill section of the mining area and the stage transportation roadway, playing an irreplaceable core role in mining operations. It is not only a key node for the transfer of coal, gangue, and materials, but also an important location for personnel movement and vehicle scheduling, having a decisive impact on the overall transportation efficiency and production safety of the mining area.
Conceptually, the lower roadway of the mining area consists of a group of roadways and chambers, including a runaway track, storage lines, connecting roadways, as well as coal bunkers, winch houses, substations, etc., all working together to ensure the functionality of the roadway. In terms of classification, based on different transportation methods, it can be divided into two categories: conveyor belt coal transportation and mine car coal transportation. Conveyor belt coal transportation is further divided into coal bunker outlet transfer and direct connection, while mine car coal transportation includes main roadway loading, stone gate loading, and detour loading. Based on the location of the material yard, it can also be divided into top-plate detour and bottom-plate detour.
(The article refers to MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, and Yuan Yong's courseware )



