Mine resources and reserve classification - Black Diamond Report
Preface
In the field of mining engineering, mine resources / Reserve classification is a crucial fundamental work, it is like a cornerstone, supporting the planning, design and operation of the entire mining activity. Accurate resource / Reserve classification can not only provide key decision-making basis for mining enterprises, but also directly relates to the rational development and utilization of resources, the realization of economic benefits and the achievement of sustainable development goals.
From a macro perspective, mine resources / Reserve classification is a scientific sorting and definition of underground mineral resources. Through classification, we can clearly understand the characteristics, quantity and usability of different types of resources. This is irreplaceable for the reasonable planning of mine construction scale, determining mining schemes, and arranging production succession. / When designing a mine, the classification of resource reserves needs to be used to determine key parameters such as mine production capacity, service life, and development methods, ensuring that the mine can produce efficiently and stably during future operations.
From a micro perspective, mine resources / Reserve classification helps mining enterprises accurately grasp the resource situation and optimize resource allocation. Different categories of resources have differences in mining difficulty, cost, and market value. Classification can be used to develop targeted mining strategies, prioritizing the mining of resources with high economic value and superior mining conditions to improve the economic benefits of enterprises. / Dynamic monitoring and updating of resource reserves also rely on a scientific classification system, which can reflect changes in resources in a timely manner and provide a basis for enterprise production adjustments.
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
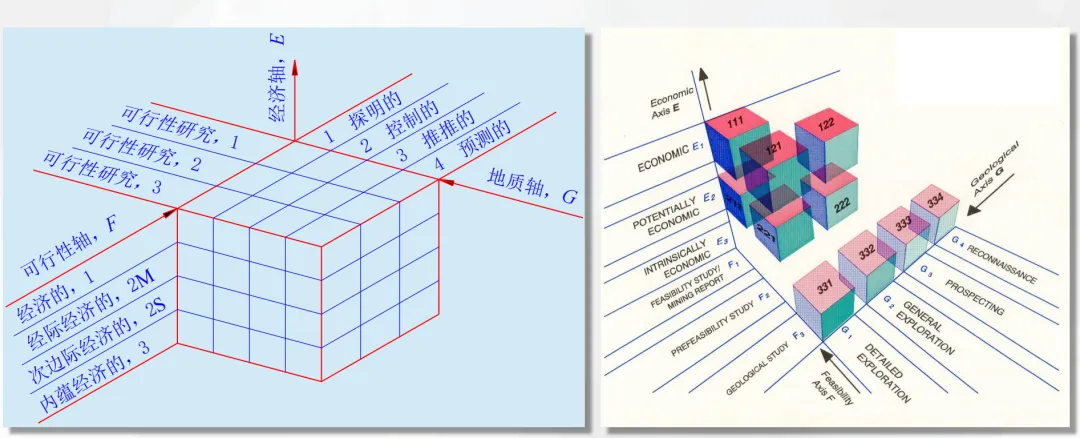
Multi-dimensional Classification
Feasibility Study Stage
Feasibility studies on mine resources / Reserve classification plays a pivotal role, mainly covering three stages: preliminary study, pre-feasibility study, and feasibility study. Each stage progresses layer by layer, having a profound impact on resource development decisions.
Preliminary research is the initial stage of feasibility evaluation, like a journey of opportunity exploration. At this stage, due to the lack of precise parameters and detailed data, researchers usually refer to the experience data accumulated by Chinese mines for a long time, such as ore grade, ore body thickness, burial depth, etc., and estimate mining costs based on the production situation of similar mines. The core purpose is to quickly judge whether there are potential investment opportunities in resource development, and provide preliminary reference for whether to conduct more in-depth exploration work or formulate long-term plans. When evaluating a newly discovered mineral area, through preliminary research, if it is found that the resource characteristics of the area are similar to those of surrounding successfully developed mines, and the preliminary estimated mining cost is within an acceptable range, it may attract investors' further attention, thus opening the door for subsequent exploration and development work. However, due to the limitations of preliminary research, the estimated resource quantity only has inherent economic significance and high uncertainty.
With the deepening of the research, we enter the pre-feasibility study stage. This stage is a preliminary exploration of the economic significance of mine development, and the results will directly determine whether the ore deposit is worth entering the exploration stage, or whether a more detailed feasibility study needs to be carried out. In pre-feasibility studies, mineral resource data obtained after detailed investigation or exploration are usually required as support, as well as laboratory-scale processing and smelting test data, and cost estimation through reference price lists or comparison with similar mine mining data. / The research content of this stage is basically the same as that of the feasibility study, but it is slightly less detailed. When evaluating a planned mine development project, pre-feasibility studies need to consider many factors, including the reliability of resource reserves, the feasibility of mining technology, market demand and price trends, etc. Only when these factors show good prospects can the project continue to advance.
Feasibility study is an in-depth analysis of the economic significance of mine development and a key basis for investment decisions. At this stage, researchers need to conduct a comprehensive and detailed analysis of resource conditions, fully considering the influence of geological, engineering, environmental, legal, and government economic policies. Specifically, in-depth investigation and detailed analysis and calculation should be carried out on aspects such as enterprise production scale, mining methods, development schemes, smelting and refining processes, product schemes, selection of major equipment, water and power supply, overall layout, and environmental protection, and multiple schemes should be compared. When determining key indicators such as investment, production and operation costs, sales revenue, profit, and cash inflow and outflow, the market price at that time should be used to ensure the timeliness and accuracy of the data. Taking the feasibility study of a large mine as an example, the research team not only needs to conduct detailed investigation of the geological structure and ore body distribution of the mine, but also needs to select the most suitable mining and smelting technology based on market demand and technological development trends, and formulate comprehensive environmental protection measures to ensure that the project is feasible in economic, technological, and environmental aspects. Only through rigorous feasibility studies can solid guarantees be provided for investment decisions, investment risks can be reduced, and effective development and utilization of resources can be achieved.
Economic Significance
Economic significance in mine resources / Reserve classification is a key dimension for measuring resource value and development feasibility. It mainly includes economic, marginal economic, sub-marginal economic, inherent economic, and undetermined economic significance. Each type reflects the economic attributes of resources from different perspectives.
Economic resources refer to those whose quantity and quality are calculated based on production indicators determined by market prices. Under current market conditions, mining technology is feasible and economically reasonable, and other conditions such as the environment are permitted. These resources have a clear development value and can bring stable returns to enterprises. The average annual value of mined products is sufficient to meet the requirements of investment returns, or development is feasible under government subsidies and (or) other support measures. Some high-quality mineral resources located in areas with convenient transportation and strong market demand have relatively low mining costs and high market prices. Mining these resources can create substantial profits for enterprises, which are typical economic resources.
Marginal economic resources are not economical to mine during current feasibility studies or pre-feasibility studies, but are close to the breakeven point. The feasibility of developing these resources largely depends on future improvements in technology, economy, environment, and other conditions, or other support policies provided by the government. Some low-grade mineral resources have high mining costs due to current limitations in mining technology, resulting in unprofitability under existing market prices. However, with technological advancements, more efficient mining and beneficiation technologies may emerge in the future, reducing mining costs; or market prices may rise, making it profitable to mine these resources. In addition, in order to encourage resource development, the government may provide tax incentives, subsidies, and other support measures, thus making marginal economic resources have development value.
The resources of sub-marginal economics are currently uneconomical and technically infeasible to exploit. Significant increases in mineral product prices or technological advancements leading to cost reductions are necessary before they become economically viable. The development of such resources faces significant challenges and requires a substantial change in external conditions. Some deeply buried mineral resources with complex ore properties are difficult to exploit effectively with current mining technologies, and the mining costs are extremely high, far exceeding what the market price can bear. Only when new mining technologies emerge that can reduce the difficulty and cost of mining, or when market demand for the mineral product increases significantly, leading to a substantial price increase, can the development of such resources be considered.
Resources with inherent economic value have only undergone preliminary investment assessments through preliminary studies and have not yet undergone feasibility studies or pre-feasibility studies. Due to numerous uncertainties, it is impossible to accurately determine whether they belong to the economic, marginal economic, or sub-marginal economic categories. In the early stages of mineral exploration, when conducting a preliminary assessment of resources in a certain area, due to limited available data, only a rough judgment of its economic significance can be made through preliminary studies. At this time, the resources in this area belong to the category of inherent economic value, and their development value requires further research and demonstration.
Resources with undetermined economic significance refer only to the predicted reserves after preliminary exploration, which belong to potential mineral resources. Their economic significance cannot currently be determined. In the preliminary exploration stage, through regional geological and (or) geophysical and geochemical anomaly research results, preliminary field observations, a very small number of engineering verification results, and analogies with known deposits with similar geological characteristics, the potentially existing reserves are predicted. However, due to a lack of sufficient exploration work and detailed data, their economic significance cannot be assessed. These resources have certain potential value, but further exploration and research are needed to determine their feasibility of development.
Geological Reliability
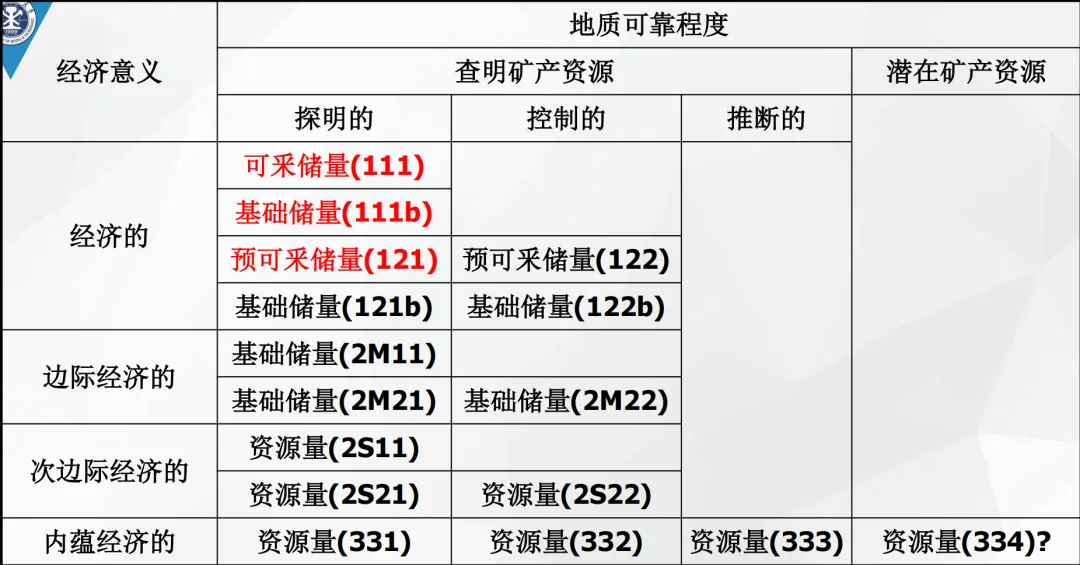
Geological reliability is an important basis for / the classification of mine resources and reserves. It reflects the differences in accuracy of the results of mineral exploration work at different stages, mainly divided into proven, controlled, inferred, and predicted types. Each type has a unique significance in resource and reserve assessment.
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
Proven geological reliability means that within the exploration area of the mine, the geological characteristics of the deposit have been thoroughly investigated through the intensification of various sampling projects. This includes the morphology, occurrence, scale, ore quality, grade, and mining technical conditions of the ore body. The continuity of the ore body has been determined, and the data used for the estimation of mineral resource quantity is detailed and highly credible. After long-term and in-depth exploration work in a certain mining area, a comprehensive and accurate understanding of all aspects of the ore body has been achieved, enabling the precise delineation of the ore body boundaries and the determination of the quality and grade distribution of the ore. The resource reserves assessed at this time have high reliability, providing a solid basis for mine design and development.
Controlled geological reliability refers to the basic clarification of the main geological characteristics, morphology, occurrence, scale, ore quality, grade, and mining technical conditions of the deposit within a certain range of the mining area according to the accuracy of detailed exploration. The continuity of the ore body is basically determined, and the data used for the estimation of mineral resource quantity is abundant and highly credible. In the detailed exploration stage, through systematic exploration work, a relatively clear understanding of the overall situation of the ore body has been obtained. However, compared to the proven stage, there may still be some uncertainties in certain details. However, the resource reserves estimated based on controlled geological reliability can already provide important references for the overall planning of the mine and the preparation of the project proposal.
Inferred geological reliability refers to the approximate clarification of the geological characteristics and the distribution characteristics, grade, and quality of the mineral deposits (points) in the reconnaissance area according to the accuracy of the reconnaissance. This also includes parts extrapolated from reserves or resources with higher geological reliability. Due to limited information and many uncertainties, the continuity of the ore body (point) is inferred, and the data used for the estimation of mineral resource quantity is limited and has low credibility. In the reconnaissance stage, through outcrop inspection, geological mapping, a limited number of sampling projects, and geophysical and geochemical methods, a preliminary understanding of the ore body has been obtained, but further exploration work is needed to verify and improve it. Resource reserves estimated based on inferred geological reliability are usually used to judge whether the area has further detailed exploration value and provide direction for subsequent exploration work.
Predicted geological reliability refers to the results obtained from preliminary exploration in areas with significant mineralization potential. When there is sufficient data and analogies can be made with known deposits with similar geological characteristics, the predicted reserves can be estimated. Predicted reserves belong to potential mineral resources and have the lowest reliability. They are mainly used in the early stages to identify areas with potential development value and provide clues for subsequent exploration work. When conducting geological surveys in a new area, through the analysis of the regional geological background and the discovery of geophysical and geochemical anomalies, it is initially judged that mineral resources may exist in the area, and the predicted reserves are estimated based on existing experience and data by analogy. However, this is only a preliminary judgment, and further exploration work is needed to confirm it.
In-depth Interpretation of Classification Codes
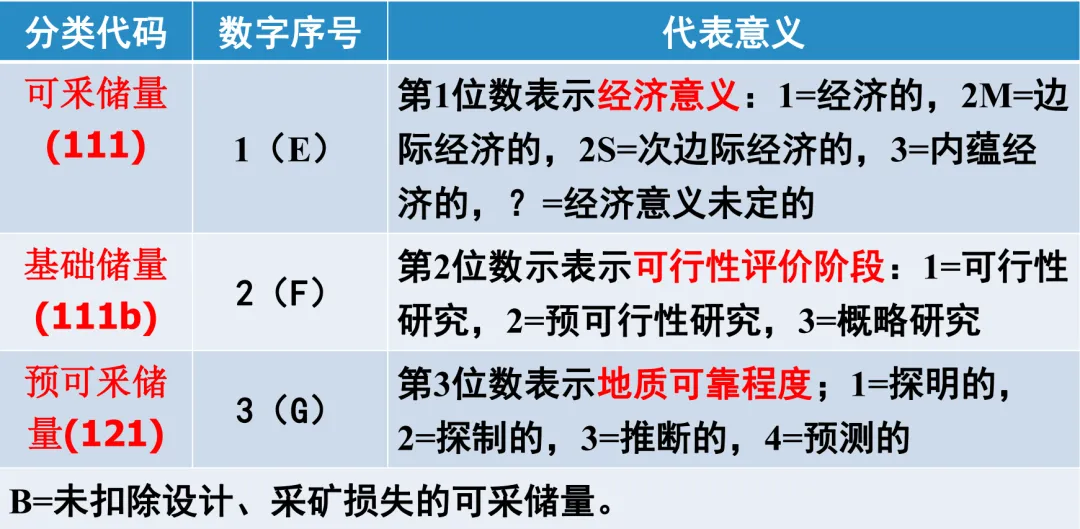
In the / reserve classification system for mine resources, 111 - 334 acts like a precise key, helping us to understand the nature and characteristics of resource reserves in depth. Each digit in these codes contains specific information. By interpreting them, we can comprehensively understand the economic significance, feasibility assessment stage, and geological reliability of the resources.
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
Taking the code 111 as an example, 1 the first digit 1 indicates that the economic significance is economic, meaning that under current market conditions, the exploitation of the resource is technically feasible, economically reasonable, and permitted by environmental and other conditions; the second digit 2 the first digit 1 indicates that the feasibility assessment stage is a feasibility study, indicating that a comprehensive and in-depth study of the resource development has been conducted, including a comprehensive consideration of geological, engineering, economic, and environmental factors; the third digit 3 the first digit 1 indicates that the geological reliability is proven, indicating that within the exploration area of the mine, the geological characteristics of the deposit have been thoroughly investigated through the intensification of various sampling projects, the continuity of the ore body has been determined, and the data used for the estimation of mineral resource quantity is detailed and highly credible. This coding method is concise and clear, capable of quickly conveying key information about the resources, and providing important basis for decision-making by mining enterprises.
Looking at the code '2M22' the first digit 1 the first digit 2M indicates marginal economics, meaning that the exploitation of the resource is not economical during the current feasibility study or pre-feasibility study, but is close to the break-even point; the second digit 2 the first digit 2 indicates the pre-feasibility study stage, indicating that a preliminary exploration of the economic significance of the deposit development has been conducted; the third digit 3 the first digit 2 This indicates the degree of geological reliability of the control, meaning that within a certain range of the mining area, the main geological characteristics, morphology, occurrence, scale, ore quality, grade, and mining technical conditions of the ore deposit have been basically ascertained according to the detailed investigation accuracy. The continuity of the ore body is basically determined, and there is a lot of data for the estimation of mineral resources, with high credibility. Through this code, we can clearly understand the development prospects and challenges of this resource, providing a reference for subsequent decision-making.
In practical applications, through the analysis of classification codes, mining enterprises can formulate corresponding development strategies according to the different characteristics of resources. For economical and proven resources, priority is given to development to obtain maximum economic benefits; for marginal or sub-marginal economic resources, strengthen technological research and development and cost control, and wait for market conditions to improve or technological progress before development; for resources with low geological reliability, increase exploration efforts, improve resource reliability, and lay the foundation for future development.
Case Analysis
Underground Coal Mine Case
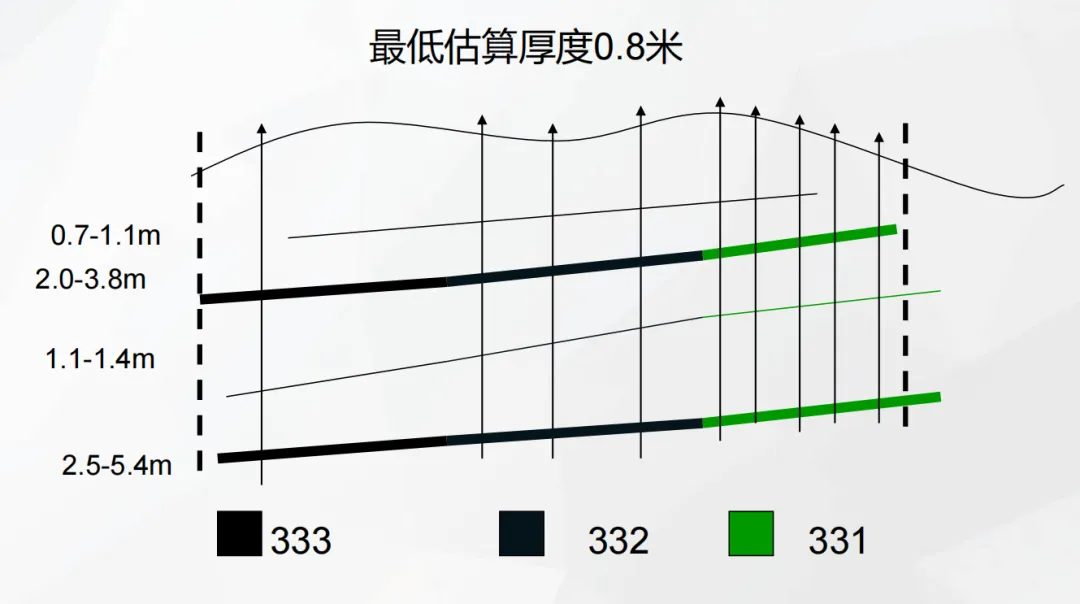
Taking a certain underground coal mine as an example, the minimum estimated thickness of this coal mine is 0.8 meters, and the minimum mineable thickness is 1.3 meters. In different areas of the mining area, different resource reserve classification situations are presented due to the differences in the detail of exploration work and geological conditions.
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
In some areas, through intensive sampling projects, the geological characteristics of the ore deposit have been thoroughly investigated, and information such as the morphology, occurrence, and scale of the ore body has been accurately grasped. The ore quality, grade, and mining technical conditions are also clearly defined, the continuity of the ore body is determined, and it meets the standard of proven geological reliability. The resource reserves in these areas are classified as 331 , that is, proven inherent economic resources. This means that at the current stage, although we have a deep understanding of the geological conditions of the resources, due to only preliminary research and no feasibility study or pre-feasibility study, there are many uncertainties, and the economic significance cannot be accurately judged, so it belongs to inherent economic resources.
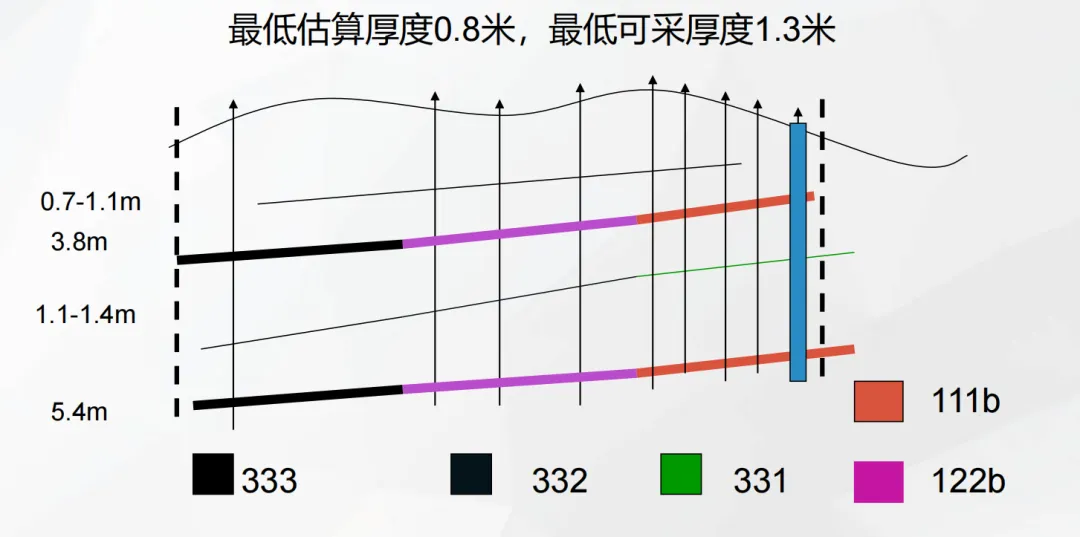
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
With the expansion of the exploration scope, the exploration work in some areas has reached the detailed investigation accuracy, and the main geological characteristics, morphology, occurrence, scale, ore quality, grade, and mining technical conditions of the ore deposit have been basically ascertained, and the continuity of the ore body is basically determined. The resource reserves in these areas are classified as 332 , that is, controlled inherent economic resources. Compared with 331 area, 332 area has a higher exploration level, more data, and higher credibility, but similarly, due to the lack of feasibility studies, the economic significance is still unclear.
In areas where exploration work is relatively weak, only preliminary exploration has been carried out through outcrop inspection, geological mapping, a small number of sampling projects, and geophysical and geochemical methods. The understanding of the ore body is preliminary, there are many uncertainties, and the continuity of the ore body is inferred. The resource reserves in these areas are classified as 333 , that is, inferred inherent economic resources. The credibility of this type of resource is low, and further exploration work is needed to verify and improve it.
The case of this underground coal mine shows that in actual mining, for 331 type of resources, because their geological conditions are clear, in subsequent feasibility studies, if their economic feasibility is determined, they can be given priority for mining; for 332 type of resources, further supplementary exploration and feasibility studies can be carried out, and the mining sequence can be reasonably arranged according to the economic evaluation results; for 333 type of resources, exploration investment needs to be increased to improve the geological reliability, and then the mining value needs to be evaluated.
Faulted Basin Coal Reconnaissance Case
When conducting coal reconnaissance in a certain faulted basin, it was found that the coal resources in this area are abundant, but the geological conditions and mining conditions in different areas are different, resulting in changes in resource reserve classification under different mining conditions and economic indicators.
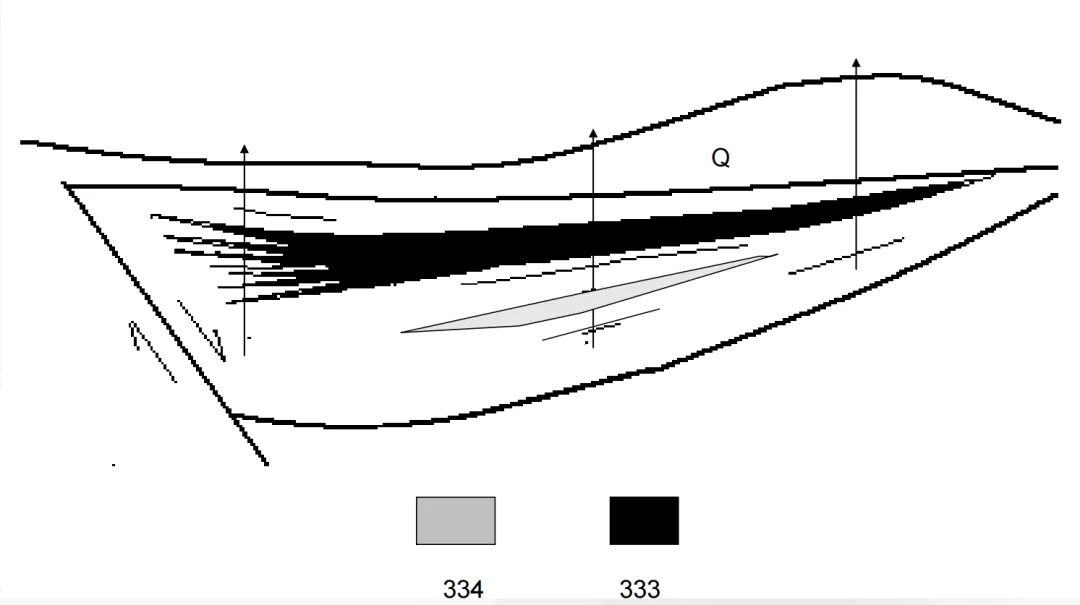
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
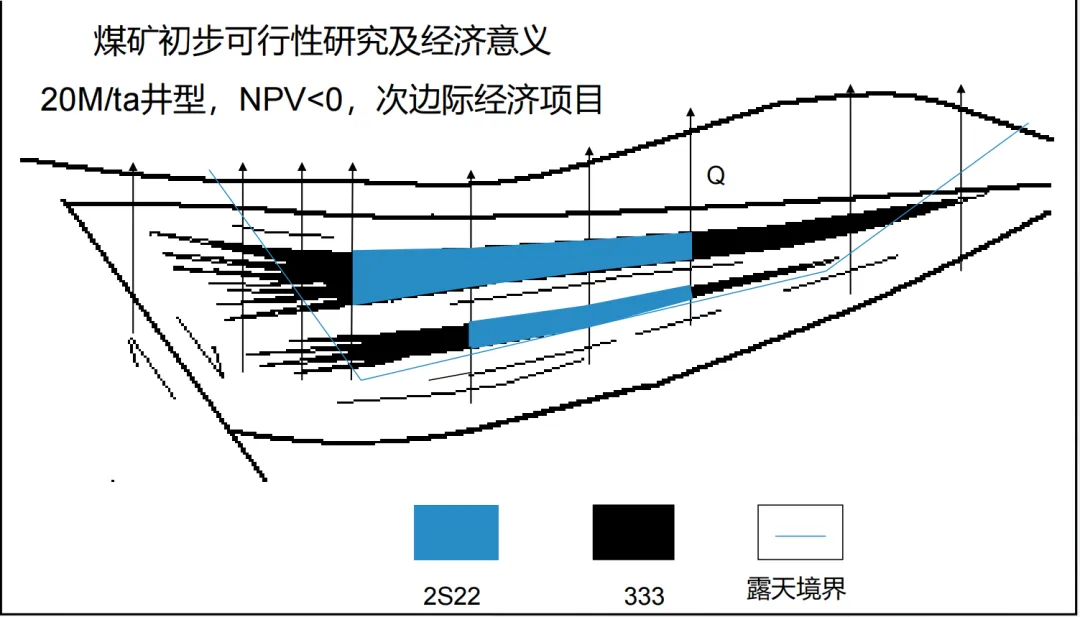
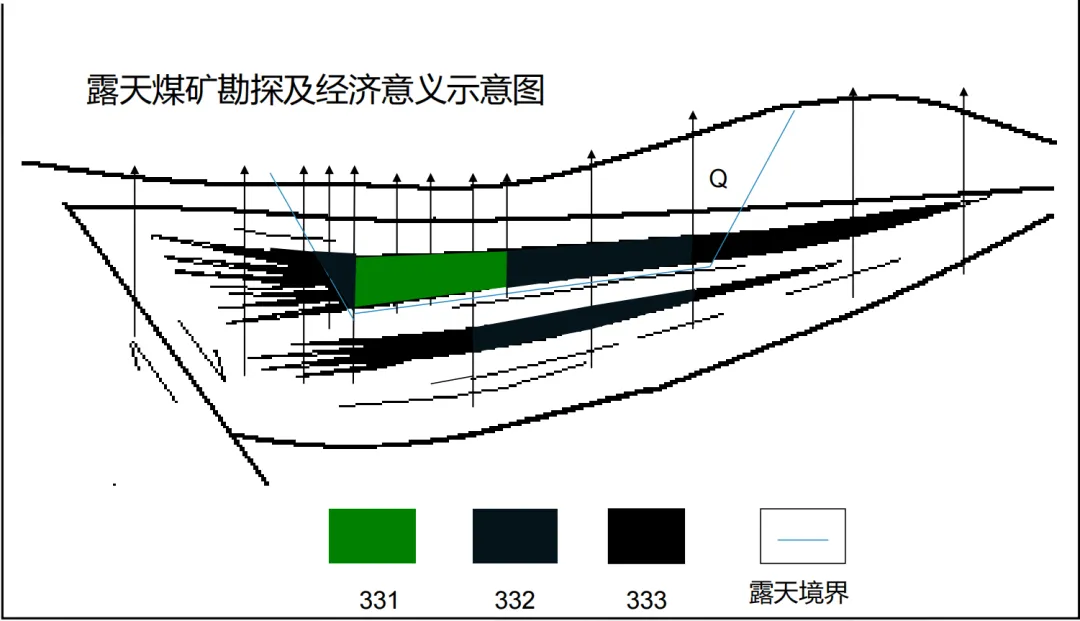
In the preliminary feasibility study stage, for a project with a designed well type of ' 20M/ta ' After evaluation, its net present value ( NPV ) is less than 0 , which is a sub-marginal economic project. In this case, part of the resource reserves in this area are classified as 2S22 , that is, sub-marginal economic, pre-feasibility study stage, controlled resources. This indicates that under the current technical and economic conditions, it is uneconomical and technically infeasible to mine these resources. It is necessary to wait for the improvement of external conditions, such as a significant increase in the price of mineral products or technological progress that reduces costs, before development is possible.
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
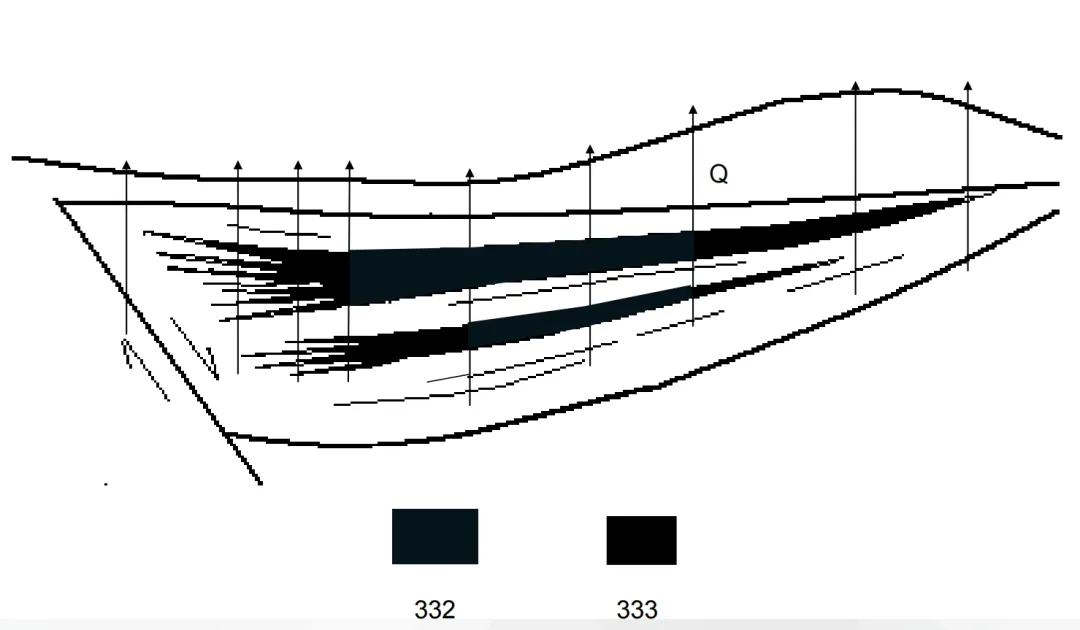
When the designed well type is adjusted to 15Mt , after re-evaluation, the net present value ( NPV ) of the project is greater than or equal to 0 , the average rate of return is greater than the internal rate of return ( IRR ) and greater than 0 , which is a marginal economic project. At this time, the resource reserve classification has changed, and some areas are classified as 2M22 , that is, marginal economic, pre-feasibility study stage, controlled resources. This shows that under the current conditions, although mining these resources is close to the breakeven point, in the future, with the improvement of technical, economic, and environmental conditions, or with government support policies, it may become economically feasible.
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
When the well type is further adjusted to ' 10Mt ' , the net present value ( NPV ) of the project is greater than or equal to 0 , internal rate of return ( IRR ) is greater than the average rate of return, which is an economic project. Correspondingly, the resource reserve classification changes again, and some areas are classified as 122b , that is, economic, pre-feasibility study stage, controlled basic reserves (recoverable reserves without deducting design and mining losses). This indicates that under this condition, mining these resources is technically feasible, economically reasonable, and environmentally permissible, and has the value of actual development.
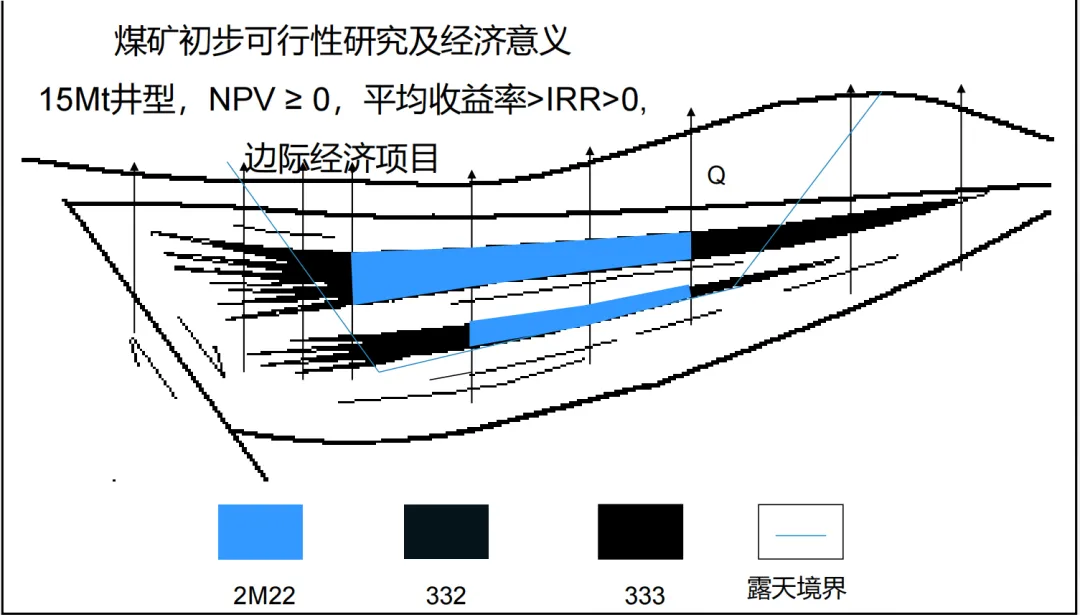
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
This case clearly shows that resource reserve classification will dynamically adjust with changes in mining conditions and economic indicators, which has a significant impact on project decision-making. In the project planning stage, various factors need to be comprehensively considered, and the resource reserve classification needs to be accurately evaluated to make scientific and reasonable decisions. For marginal and sub-marginal economic projects, the future development potential and risks need to be carefully evaluated, while for economic projects, the development process can be accelerated to achieve effective resource utilization and maximize economic benefits.
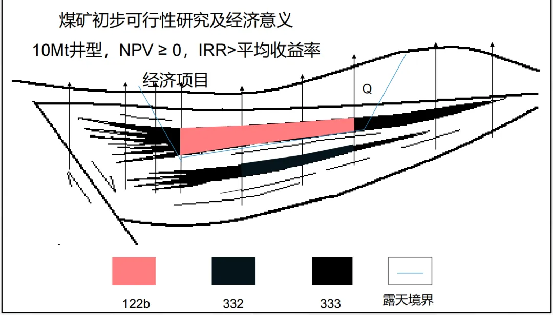
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
Open-pit coal mine case
When classifying resource reserves and designing mining schemes for a certain open-pit coal mine, factors such as geological conditions, resource distribution, and economic feasibility were fully considered. Through detailed geological exploration, the coal mine has gained a comprehensive understanding of the distribution, thickness, and quality of coal seams in the mining area.
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
In terms of resource reserve classification, based on the exploration results, in some areas, due to detailed exploration work, the geological characteristics of the ore deposit have been identified, the continuity of the ore body has been determined, and feasibility studies have been conducted to determine the economic rationality of mining. The resource reserves in these areas are classified as 111b,即经济的、可行性研究阶段的、探明的基础储量(未扣除设计、采矿损失的可采储量)。而在一些勘查程度稍低,但基本查明了矿床主要地质特征的区域,资源储量被划分为 332,即控制的内蕴经济资源量。在勘查工作相对较少的区域,资源储量则被划分为 333,即推断的内蕴经济资源量。
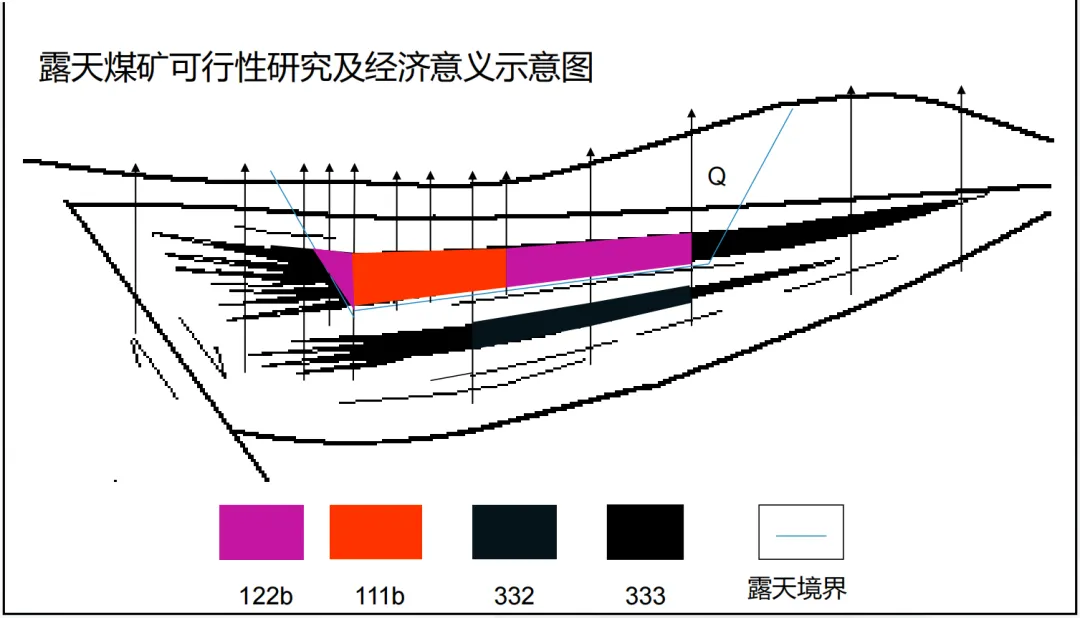
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )
In terms of mining scheme design, open-pit coal mines have their own characteristics. Because the ore body is buried relatively shallow, the open-pit mining method can fully utilize resources and improve mining efficiency. In the mining process, stripping operations are first carried out to remove the topsoil and rocks covering the ore body, and then mining operations are carried out. Through reasonable planning of the mining sequence and transportation routes, the efficient progress of mining work is ensured. The use of large excavators and transport vehicles enables the rapid transportation of ore from the mining site to the concentrator for processing.
From the perspective of economic feasibility, the mining cost of open-pit coal mines is relatively low, and the production capacity is large. Because open-pit mining can directly expose the ore body, it is convenient to use large-scale equipment for operation, which greatly improves mining efficiency and reduces unit cost. Compared with underground coal mines, open-pit coal mines have lower ventilation and drainage costs, and can better achieve comprehensive resource utilization and improve economic benefits. Open-pit coal mines also have advantages in resource utilization, enabling more complete recovery of useful components in the ore and reducing resource waste.
Impact of mine resource reserve classification
Key guidance for mining decisions
Mine resource reserve classification plays a crucial guiding role in mining decisions. In terms of mining scheme selection, different resource reserve categories and geological conditions determine the differences in mining methods. For ore bodies with abundant reserves, stable geological conditions, and shallow burial, open-pit mining is often the preferred scheme, as this method can fully utilize resources, improve mining efficiency, and reduce costs. As mentioned in the previous open-pit coal mine case, through detailed classification and exploration of resource reserves, the distribution and characteristics of the ore body were determined, thus adopting open-pit mining methods to achieve efficient resource development. For ore bodies with deep burial and complex geological conditions, underground mining methods need to be adopted, and appropriate coal mining methods should be selected according to the specific situation, such as fully mechanized mining, ordinary mining, or blasting mining.
Equipment selection also closely depends on mine resource reserve classification. The scale of resource reserves and mining conditions determine the type and specifications of equipment required. For large-scale resource reserves, large and efficient mining equipment needs to be equipped to improve production efficiency and reduce costs. In large coal mines, the use of large coal mining machines, scraper conveyors, and hydraulic supports can achieve high-yield and high-efficiency mining. For small mines or areas with limited resource reserves, small and flexible equipment can be selected to adapt to different mining needs.
Production planning also relies on the guidance of mine resource reserve classification. Accurate resource reserve data is an important basis for determining production scale, mining sequence, and mining progress. Through the analysis of resource reserves, the mining time and output of each mining area can be reasonably arranged to ensure the continuity and stability of mine production. Prioritizing the mining of resources with high economic value and good mining conditions can not only guarantee the economic benefits of the enterprise but also provide guarantees for subsequent mining work. When formulating production plans, it is also necessary to consider the changes in resource reserves and adjust the plans in a timely manner to adapt to the needs of actual production.
The core role in resource management and sustainable development
Mine resource reserve classification plays an irreplaceable core role in resource management and sustainable development. In terms of reasonable resource planning, it provides a scientific basis for the optimal allocation of resources. Through the classification and evaluation of resource reserves, it is possible to clearly understand the distribution and characteristics of different types of resources, thereby formulating reasonable mining plans to avoid resource waste and over-exploitation. For economic and proven resources, priority is given to mining to fully utilize their economic value; for marginal or sub-marginal economic resources, reasonable development is carried out when technical and economic conditions permit; for resources with lower geological reliability, exploration work is strengthened to improve resource reliability and lay the foundation for future development.
In terms of resource protection, mine resource reserve classification helps to achieve effective resource protection. Through dynamic monitoring and analysis of resource reserves, it is possible to promptly identify problems in the resource mining process and take corresponding measures to solve them. In the mining process, the loss rate of resources is strictly controlled, the recovery rate of resources is improved, and resource waste is reduced. Reasonably plan mining areas to avoid damage to the surrounding environment and ecology, and achieve coordinated development of resource development and environmental protection.
From the perspective of sustainable development, mine resource reserve classification is crucial to the long-term development of the mining industry. It provides a basic guarantee for the sustainable development of the mining industry and ensures the long-term stable supply of resources. Through scientific resource reserve classification and management, it is possible to reasonably arrange the mining and utilization of resources, extend the service life of mines, and promote the sustainable development of the mining industry. Strengthening the comprehensive utilization of resources, improving the added value of resources, and achieving efficient and cyclical utilization of resources are also important measures for the sustainable development of the mining industry.
Summary
Mine resources / Reserve classification is a key link in the field of mining engineering. It is based on multi-dimensional criteria such as the feasibility evaluation stage, economic significance, and geological reliability, and constructs a scientific and rigorous classification system. Through an in-depth interpretation of the classification codes and analysis of practical cases, we clearly understand its core role in mining decisions, resource management, and sustainable development.
(Picture from MOOC China University of Mining and Technology Mining Engineering Tu Shihao, Fang Zhijun, Zheng Xigui, Wang Xufeng, Peng Hongge, Yuan Yong )

Previous Page


