Mine transportation single vein roadway layout - Black King Kong report
I. Introduction
In the complex system of mine excavation, the stage transportation roadway acts like the arteries of the human body, undertaking the crucial task of ore transportation. Its layout directly affects the efficiency, cost, and safety of mine production. A reasonable layout of stage transportation roadways can efficiently transport ore from the mining area to the hoisting shaft or concentrator, ensuring the continuity of mine production; conversely, an unreasonable layout may lead to low transportation efficiency, increased costs, and even affect the normal production of the mine. Among the numerous layouts of stage transportation roadways, the single vein roadway layout, with its unique advantages and applicable conditions, plays an important role in specific mine excavation scenarios.
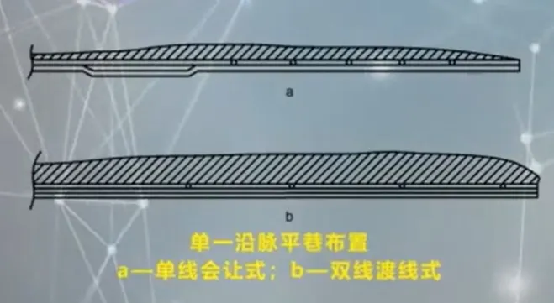
(Image from MOOC Northeastern University Underground Mining of Metal Deposits Xu Shuai, An Long )
II. Types of Single Vein Roadway Layouts
(1) Single-line Passing
The single-line passing route design is relatively simple; except for the passing station, the entire transportation roadway is a single line. During actual operation, when a loaded vehicle travels along the single line, the empty vehicle needs to wait and give way at a specific passing station, and vice versa. This route setting is like a one-way street, where vehicles can only pass in sequence; only at a specific " passing area ” " can vehicles pass each other. The single-line passing system has a low capacity, mainly because its single-line design limits the parallel operation of vehicles. At the same time, only vehicles in one direction can travel in the transportation roadway. Once a situation of two-way vehicle intersection occurs, one party needs to wait at the passing station, which greatly increases the time cost of transportation and reduces transportation efficiency.
In thin ore body mining, due to the small scale of the ore body and the relatively low ore output, the throughput capacity of the transportation roadway is not high. Although the single-line passing system has limited throughput capacity, it is sufficient to meet the transportation needs of thin ore body mining. Moreover, its simple route setting and low construction cost make it have a high cost-effectiveness ratio in thin ore body mining. In some medium-thick ore body mining, if the exploration degree of the ore deposit is insufficient, the future ore output is conservatively estimated, or the production scale of the mine itself is small, the single-line passing system can also exert its advantages. It can reduce initial construction investment and mine development costs while meeting current transportation needs.
(2) Double-line Crossing
The double-line crossing system has double lines in the transportation roadway, which is like a two-way road in a city, where vehicles can travel in both directions simultaneously, greatly improving transportation efficiency. In order to achieve flexible conversion of vehicles between the two lines, crossing lines are set up at appropriate locations. The crossing lines are like ramps connecting two main roads, allowing vehicles to switch from one line to another, enabling the meeting and passing of vehicles in different directions. The double-line crossing system has a large throughput capacity because the double-line setting allows vehicles to travel in both directions simultaneously, reducing waiting time. The reasonable setting of crossing lines also provides more flexibility for vehicle scheduling and passing. When a certain line is congested or needs special operations, vehicles can switch to another line through the crossing line to ensure the continuity of transportation.
Annual output 20 - 60 Ten thousand tons of mines have a relatively large ore output and have high requirements for the throughput capacity of the transportation roadway. The double-line crossing system can meet the transportation needs of this scale of mines and ensure that the ore can be transported efficiently and promptly to the designated location. If a single-line passing system is used, the insufficient throughput capacity may lead to ore backlog and affect the mine's production progress. The efficient transportation capacity of the double-line crossing system can avoid this situation and ensure the normal production of the mine.
III. Single Vein Roadway Layout - Extra-vein Layout
(1) Applicable Conditions
When the ore is poorly consolidated, if roadways are laid inside the ore body, the ore cannot provide stable support, and the roadway is prone to collapse and deformation, seriously affecting the safety and efficiency of transportation. By laying the roadway outside the vein in a stable surrounding rock, the stable surrounding rock can be used to bear the pressure of the roadway, ensuring the stability of the roadway. In some gold mine excavations, if the ore structure of the gold ore body is loose and poorly consolidated, but the surrounding rock has high hardness and good stability, the extra-vein layout can effectively avoid the problems of roadway maintenance caused by poor ore consolidation.
For high-grade ore, extra-vein layout can reduce damage to the ore body and maximize the integrity and grade of the ore. During the excavation process, if roadways are excavated inside the ore body, it will inevitably cause some disturbance and damage to the ore body, leading to the loss of some high-grade ore or the mixing of other impurities, reducing the grade of the ore. The extra-vein layout can avoid this situation, ensuring the quality of high-grade ore and improving the economic benefits of the mine.
(2) Advantages
In terms of roadway maintenance, the stable surrounding rock provides a solid support base for the roadway. The stability of the surrounding rock ensures that the roadway can withstand various external forces such as pressure from the overlying rocks, ground stress, and vibrations generated by the operation of transportation equipment during long-term use, and is not prone to deformation or collapse. This reduces the work of frequent maintenance and repair of the roadway, reduces maintenance costs, and improves the service life of the roadway. Compared with intra-vein layout, the maintenance cycle of extra-vein roadways can be extended several times, and maintenance costs can also be reduced significantly.
The existence of ore pillars is to support the ore body and prevent the ore body from collapsing during excavation, but the existence of ore pillars also leads to the inability to excavate some ore, resulting in resource waste. When using extra-vein layout, because the roadway is not inside the ore body, the damage to the integrity of the ore body is relatively small, and the number of ore pillars set up for roadway maintenance can be reduced, thereby reducing ore pillar loss. In the excavation of some medium-thick ore bodies, the use of extra-vein layout can reduce the ore pillar loss rate by 10% - 20% , greatly improving the ore recovery rate and reducing resource waste.
IV. Single Vein Roadway Layout - Intra-vein Layout
(1) Applicable Conditions
In regular medium-thick ore bodies, the morphology of the ore body is relatively stable, with less variation in strike and thickness. This allows for better assurance of the stability and continuity of roadways during excavation within the ore body, facilitating subsequent mining operations. When the output is not large, the requirements for the throughput capacity and transportation efficiency of the haulage roadways are relatively low. Intra-vein layout can meet the transportation needs of this small-scale production, while also utilizing its own advantages, such as convenient prospecting and loading, to improve the overall efficiency of mine mining.
If the ore deposit exploration is insufficient, excavating roadways within the ore body can play a supplementary exploration role to a certain extent. By observing and analyzing the ore body conditions revealed during roadway excavation, more geological information about the ore body can be obtained, such as ore grade changes and geological structures, providing a more accurate basis for subsequent mining decisions. When the ore grade is low, the economic value of the ore is relatively low, and controlling mining costs is more important. Intra-vein layout can incidentally mine ore during excavation, reducing the amount of excavation work specifically for mining ore, thereby reducing excavation costs and improving the economic efficiency of mine mining. In cases where it is not necessary to recover ore pillars, intra-vein layout will not affect mining efficiency and ore recovery rate due to the presence of ore pillars. The presence of ore pillars may result in some ore being unable to be mined, causing resource waste, while intra-vein layout can avoid this situation and improve ore recovery rate.
(II) Advantages and Limitations
In terms of prospecting, intra-vein roadways are excavated directly in the ore body, which can intuitively reveal the geological characteristics of the ore body. Through observation and sampling analysis of the ore body on the roadway walls, information on ore grade changes, ore structure, and tectonics can be obtained, providing first-hand data for further geological exploration and mining scheme development. In some metal mines, the excavation of intra-vein roadways has discovered new ore body branches and rich ore sections, providing more resource guarantees for the continuous mining of the mine.
Intra-vein roadways are closely connected to the ore body, and the ore mined from the stope can be directly loaded into the haulage vehicles in the roadway through chutes or other transportation equipment, reducing the transfer links during ore transportation and improving loading efficiency. This not only saves time and labor costs but also reduces ore loss and impoverishment during transfer.
Since ore can be incidentally mined during excavation, this mined ore can be directly sold or enter the beneficiation process, bringing certain economic benefits to the mine. These benefits can be used to offset some excavation costs, reducing the mine's upfront investment costs. In some small mines, through intra-vein layout, a large amount of ore has been mined during the excavation phase, alleviating the mine's financial pressure and providing financial support for subsequent mining work.
When the ore body changes significantly along the strike, in order to adapt to the changes in the ore body, the intra-vein roadways have to bend accordingly. Bent roadways will increase the running resistance of transportation equipment, reduce transportation speed, and also increase the wear and tear and failure probability of transportation equipment, affecting transportation efficiency and safety. When using mine locomotives for transportation, bent roadways will make the driving stability of the mine locomotives worse, easily causing derailments and other accidents, requiring frequent maintenance and repairs, increasing transportation costs and management difficulty.
V. Application Case Analysis of Single Intra-Vein Roadway Layout
(I) Case Selection
Shouyun Iron Mine, as the largest metal mine in Beijing, has a long history of mining, and its mining technology and experience are representative in the industry. In its mining process, it faces the problem of recovering open-pit slope hanging ore, including Ⅲ Blind ore zone 7# Ore body is a typical isolated thin ore body, located 28 - 30m away from the main ore body, along the strike 93m dip angle 76 - 81° thickness 2 - 8.3m located between + 104m and + 68m , with an ore quantity of approximately 4.2 ten thousand tons. The mining conditions of this isolated thin ore body are complex, and high requirements are placed on the layout of the haulage roadways. Shouyun Iron Mine adopted a single intra-vein roadway layout in the mining of this ore body, providing a good case for studying the effect of this layout in practical applications.
(II) Application Status Introduction
In Ⅲ Blind ore zone 7# the mining of the ore body, Shouyun Iron Mine adopted a single ore-out entry stage mining method, with only one intra-vein roadway laid at the bottom of the ore body. This intra-vein roadway serves as both a bottom roadway and an ore-out roadway. From the perspective of route setting, due to the relatively small scale of the ore body and limited transportation volume, a single-line passing route layout was adopted. In practical applications, the ore mined from the stope is concentrated to the intra-vein roadway through gravity or other simple transportation methods, and then the ore is transported out along the single-line roadway by transportation equipment. In the setting of the passing station, the location of the passing station is reasonably determined according to the length of the roadway and the running time interval of the transportation equipment to ensure that the loaded and empty vehicles can pass each other in an orderly manner, improving transportation efficiency.
This layout has achieved significant application results. In terms of cost, due to the reduction of bottom structure preparation engineering, compared with the multi-entry stage mining method, the mining ratio is significantly reduced, thereby reducing mining costs. In terms of mining cycle, the simplified roadway layout makes the mining preparation work faster, shortening the mining cycle and improving the mine's production efficiency.
(III) Experience and Enlightenment
The Shouyun Iron Mine case shows that when mining isolated thin ore bodies, a single intra-vein roadway layout, under the premise of meeting the mining conditions of the ore body, can effectively reduce costs and shorten the mining cycle. For other mines facing similar ore body mining, if the ore body scale is small, the transportation volume is not large, and there are high requirements for cost control and mining efficiency, they can learn from the experience of Shouyun Iron Mine and give priority to the single intra-vein roadway layout. When adopting a single-line passing route, the location and spacing of the passing station should be reasonably planned to ensure smooth transportation. According to the specific situation of the ore body, the functions and layout of the roadway should be flexibly adjusted to fully utilize the advantages of the single intra-vein roadway layout.
VI. Factors Affecting the Layout of Single Vein-Following Haulage Ways
(A) Orebody-Related Factors
The thickness of the orebody has a significant impact on the layout of single vein-following haulage ways. When the orebody thickness is less than 4 - 15 meters, due to the relatively small scale of the orebody and the small amount of ore transportation, a single vein-following haulage way can meet the transportation needs. In some thin orebody lead-zinc mine mining operations, the orebody thickness is usually within a few meters. Using a single vein-following haulage way layout, whether it is a single-line passing or double-line crossing, can effectively transport the ore from the mining face.
The stability of the ore and rock is an important factor that must be considered in the layout of the haulage way. For in-vein layout, if the ore and rock stability is poor, the haulage way is prone to collapse and deformation during excavation and use, seriously affecting transportation safety and efficiency. When mining some fragmented gold orebodies, due to the poor stability of the ore and rock, using an in-vein layout will lead to frequent collapses of the haulage way, requiring a large amount of support and repair work, increasing the mining cost and safety risks. For extra-vein layout, good surrounding rock stability is an important prerequisite for its implementation. Only when the surrounding rock can provide stable support can the long-term stability of the haulage way be ensured, reducing maintenance costs.
The dip angle of the orebody will also affect the layout of the single vein-following haulage way. When the dip angle of the orebody is gentle, more auxiliary equipment may be needed during ore transportation to ensure smooth transportation, which will increase transportation costs and complexity. In some gently inclined coal mining operations, special transportation equipment and technologies, such as belt conveyors, are needed to overcome the difficulty of ore sliding. When the dip angle of the orebody is steep, gravity can assist ore transportation, but it is also necessary to consider how to control the sliding speed of the ore to ensure transportation safety.
(B) Production Factors
The production capacity of the mine is one of the key factors determining the layout of a single vein-following haulage way. For mines with an annual output of 20 - 60 ten thousand tons, a double-line crossing layout of a single vein-following haulage way can meet its large transportation needs. The large throughput capacity of the double-line crossing layout can ensure that more ore is transported per unit of time, meeting the high production capacity requirements of the mine. For mines with smaller output, the single-line passing layout is more economical and reasonable. Although its throughput capacity is limited, its construction cost is low, and it can meet the transportation needs of small-scale production while reducing the mine's initial investment.
The choice of mining method is closely related to the layout of a single vein-following haulage way. Different mining methods have different mining face structures and ore extraction methods, which require the layout of the transportation haulage way to adapt to them. When using open-stoping, the mining face usually has a large space, and the ore extraction points are relatively concentrated, which requires the transportation haulage way to be easily connected to the mining face to ensure that the ore can be transported out in time. When using caving mining, because the mining face roof will collapse naturally or forcibly, the transportation haulage way needs to be laid in a safe location to avoid being affected by the collapsed rocks.
Good ventilation is an important condition for ensuring the safety of underground workers and improving production efficiency. The layout of a single vein-following haulage way needs to consider ventilation requirements to ensure clear ventilation and return air routes. The layout of the haulage way should minimize turns and avoid sudden expansion or contraction of the haulage way cross-section to reduce ventilation resistance. In some mines, by rationally planning the direction and connection method of the single vein-following haulage way, it is organically combined with the ventilation system, achieving smooth circulation of fresh air and effective discharge of foul air, creating a good environment for underground operations.
VII. Comparison with Other Stage Transportation Haulage Way Layout Forms
(A) Selection of Comparison Objects
In the field of mine mining, the layout forms of stage transportation haulage ways are diverse, each with its unique advantages and applicable scenarios. In order to more comprehensively and deeply understand the characteristics of the single vein-following haulage way layout, we select the lower-level double haulage way plus connecting passage, extra-vein flat haulage way plus crosscut, etc., as comparison objects. The lower-level double haulage way plus connecting passage layout sets up loading haulage ways and traveling haulage ways in the lower-level surrounding rock contact zone and surrounding rock respectively, and connects them with connecting passages, forming a unique transportation system; the extra-vein flat haulage way plus crosscut layout sets up double-line traveling flat haulage ways in the lower-level surrounding rock, and sets up single-line loading crosscuts at intervals. Through comparative analysis of these layout forms, we can more clearly show the performance of the single vein-following haulage way layout in different aspects, providing a strong reference basis for the selection of transportation haulage way layout forms in mine mining.
(B) Comparison Content
1. Throughput Capacity : In the single vein-following haulage way layout, the single-line passing method, because the transportation haulage way is single-line except for the passing station, loaded and empty vehicles need to alternate, resulting in a small throughput capacity, and it is easy to have long waiting times during busy transportation, affecting transportation efficiency. Although the double-line crossing method sets up double lines and connects them through crossing lines, the throughput capacity is improved, and it can be used for mines with an annual output of 20 - 60 ten thousand tons, but there is still a certain gap compared with the lower-level double haulage way plus connecting passage and extra-vein flat haulage way plus crosscut layouts. In the lower-level double haulage way plus connecting passage layout, the loading haulage way and traveling haulage way are set separately, and the vehicles do not interfere with each other, greatly improving the smoothness and throughput capacity of transportation, suitable for large-scale mining of medium-thick and medium-thick and above orebodies. The extra-vein flat haulage way plus crosscut layout uses a combination of double-line traveling flat haulage ways and single-line loading crosscuts, with a larger stage transportation capacity, which can meet the transportation needs of thick orebody mines with an annual output of 60 - 150 ten thousand tons.
2. Applicable Orebody Types : The in-vein form of the single vein-following haulage way layout is suitable for regular medium-thick orebodies with small output, insufficient orebody exploration, low ore grade, and no need to recover ore pillars. When the orebody changes greatly along the strike, the haulage way of the in-vein layout will bend to adapt to the orebody changes, which is not conducive to the operation of transportation equipment. The extra-vein form is suitable for orebodies with poor ore stability, high grade, and stable surrounding rock, which can effectively utilize the stability of the surrounding rock, reduce haulage way maintenance costs, and ore pillar losses. The lower-level double haulage way plus connecting passage layout is suitable for medium-thick and medium-thick and above orebodies. Its unique haulage way setting method can adapt to the mining needs of large-scale orebodies, and it is also conducive to vehicle travel, ore loading, and ore exploration. The extra-vein flat haulage way plus crosscut layout is mostly used for thick orebodies. When mining thick orebodies on a large scale, it can fully exert its advantages of large stage transportation capacity and convenient and safe ore loading, and can also conduct lateral exploration to a certain extent.
3. Excavation Amount Single-vein roadway layouts are relatively simple, whether they are in-vein or out-vein layouts, the excavation workload is relatively small. In the mining of some thin or medium-thick ore bodies, using a single-vein roadway layout can reduce unnecessary roadway excavation and lower mining costs. The lower-level double-lane layout with connecting roadways requires simultaneous excavation of loading roadways and haulage roadways, and connecting roadways must be set at regular intervals, significantly increasing the excavation workload. The out-vein level roadway plus crosscut layout not only requires the excavation of double-track haulage level roadways but also requires the layout of single-track loading crosscuts at regular intervals on the level roadways, resulting in an even larger excavation workload.
4. Safety In a single-vein roadway layout, the single-line yielding system has a relatively concentrated safety risk in the yielding station due to its simple route. If the dispatching of the yielding station has problems, it is easy to cause collisions and other safety accidents. Although the double-line crossing system has improved throughput, there are still some safety hazards in the crossing area, such as improper turning operations of vehicles at the crossing point may lead to derailment accidents. In the lower-level double-lane layout with connecting roadways, the loading line and haulage line are separated, and the vehicles do not interfere with each other, making transportation safe and convenient, effectively reducing the probability of vehicle collisions and other accidents. In the out-vein level roadway plus crosscut layout, the connection method between the crosscut and the level roadway is relatively safe during ore loading, reducing the safety risks during ore loading.
Comparison Conclusion
In terms of throughput, the single-vein roadway layout has certain disadvantages compared to the lower-level double-lane layout with connecting roadways and the out-vein level roadway plus crosscut layout, especially the single-line yielding system, which is difficult to meet the transportation needs of large-scale mines. In terms of applicable ore body types, the single-vein roadway layout has certain specificity. In-vein layouts are suitable for medium-thick ore bodies under specific conditions, while out-vein layouts are suitable for ore bodies with different ore and surrounding rock stability, showing strong adaptability. In terms of excavation volume, the single-vein roadway layout has obvious advantages. The smaller excavation volume means lower costs and shorter construction periods. In terms of safety, although there are some risk points, safe transportation can still be ensured under reasonable scheduling and management.
When selecting the layout of the stage transportation roadway, mining enterprises need to comprehensively consider various factors such as ore body type, production scale, excavation cost, and safety requirements, weigh the pros and cons, and choose the most suitable layout for their own situation to achieve efficient, safe, and sustainable development of mine mining.
Summary
Single-vein roadway layouts have a unique position and role in mine mining. Its single-line yielding system and double-line crossing system line settings, as well as in-vein and out-vein layout methods, provide diversified choices for mines with different mining conditions. In practical applications, such as in the mining of the Shouyun Iron Mine, Ⅲ Blind ore zone 7# ore bodies, it fully demonstrates the advantages of single-vein roadway layouts in reducing costs and shortening mining cycles. Many factors affect the layout of single-vein roadways, including ore body thickness, ore and rock stability, ore body dip angle, production capacity, mining methods, and ventilation requirements. These factors are interrelated and jointly determine the rationality and effectiveness of the single-vein roadway layout. Compared with the lower-level double-lane layout with connecting roadways and the out-vein level roadway plus crosscut layout, the single-vein roadway layout has both advantages and disadvantages in terms of throughput, applicable ore body types, excavation volume, and safety.
Note: Part of the content of this article refers to MOOC Northeastern University Underground Mining of Metal Deposits Xu Shuai, An Long's courseware



